3d graphic design software
best free graphic design software
best graphic design software free
c# graphics library
download design
download free graphic design software
free graphic design
free graphic design programs
1. Getting to Know CAD: The Heart of Modern Design
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design, a software program that has replaced traditional paper, pencil, and drafting tables.
- Definition: CAD is a computer program that allows designers, architects, and engineers to create, edit, analyze, and visualize 2D and 3D models quickly and accurately.
- Popular Programs: The world's most standard and widely used CAD program is AutoCAD from Autodesk, the primary choice for professionals in many industries.
2. Why is CAD so important and useful?
Using CAD software doesn't just change the tools; it revolutionizes the workflow, dramatically improving efficiency.
- Improved speed: Creating and editing designs is much faster than manually drawing, and the design is easily reused.
- Improved accuracy: Using a coordinate system and numerical drawings ensures that designs are perfectly accurate to the specified scale and dimensions.
- Clear presentation: Creating realistic 3D models allows for a clear visualization of a project or building before actual production or construction.
- Reducing errors and costs: Simulating and verifying designs on a computer before actual construction allows for easy error detection and cost savings in manufacturing defects.
3. In which industries is CAD used?
CAD is an essential tool used in virtually every industry related to design and manufacturing:
- Architecture & Construction: Designing house plans, buildings, structures, and systems.
- Mechanical Engineering: Designing machinery components, spare parts, and various products.
- Civil & Electrical Engineering: Designing bridges, roads, electrical systems, and plumbing.
- Product Design: Designing consumer products such as furniture and electronic devices.
4. Basics for Beginners: Essential Commands to Know
To begin 2D drafting in AutoCAD (which forms the basis of most design work), you need to familiarize yourself with these core tools:
Drawing Tools
- LINE (L) is used to draw straight lines, which are the foundation for creating various shapes.
- CIRCLE (C) is used to draw circles, defined by their radius or diameter.
- ARC (A) is used to draw curves, defined by their starting point, second point, and end point.
Editing Tools
- OFFSET (O) is used to create parallel lines from existing lines, specifying the desired distance (very common!).
- TRIM (TR) is used to trim unwanted lines, provided another line intersects them.
- EXTEND (EX) is used to extend a line so that it meets a specified reference line.
- MOVE (M) is used to move an object from one location to another.
Sizing
- DIMENSION (Linear/Angular) is used to define and display the dimensions (length, angle) of an object in the drawing.
5. Coordinate System: The Heart of Accuracy
In CAD programs, every line and point is defined using a coordinate system, which ensures the highest possible design accuracy.
- WCS (World Coordinate System): This is the program's primary coordinate system (fixed X, Y, and Z axes).
- UCS (User Coordinate System): This is a user-defined coordinate system that facilitates drafting in different orientations, especially in 3D work.
Core Topics
- CAD, AutoCAD, Drafting, Design, 2D, 3D
Skill Level
- Beginner, Basic, Complete Guide
Content Type
- Overview, Introduction, Basic Commands, Industry
Application
- Architecture, Engineering, Product Design
CAD, AutoCAD, Drafting, Beginner, Basic CAD, 2D, 3D, Engineering, Architecture
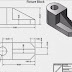
Figure 1: CAD Overview. This image illustrates the core concepts of CAD, with a 3D model of a building or machine part in the center, accompanied by small icons representing design tools and the computer running the CAD program in the background.
Figure 2: CAD Applications in Industry. This image shows small 3D icons representing various industries, such as buildings (architecture), gears (mechanical engineering), roads (civil engineering), and products (product design), surrounding CAD symbols or 2D plans.
Figure 3: Differences between 2D and 3D in CAD. This image presents a comparison between a 2D plan (a flat room plan) and a 3D plan (a room model with depth) to demonstrate CAD's ability to create more realistic images.
Figure 4: Basic CAD Tool Icons. This image shows 3D icons for basic CAD commands, such as LINE, CIRCLE, OFFSET, TRIM, and DIMENSION, to represent important tools that beginners should know.